News Release
- Astemo, Ltd.
- FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Astemo develops new rare-earth-free motor that reduces resource risks
Combination of rare-earth-free magnets and synchronous reluctance motors from main drives and auxiliary drives enables a wide range of outputs
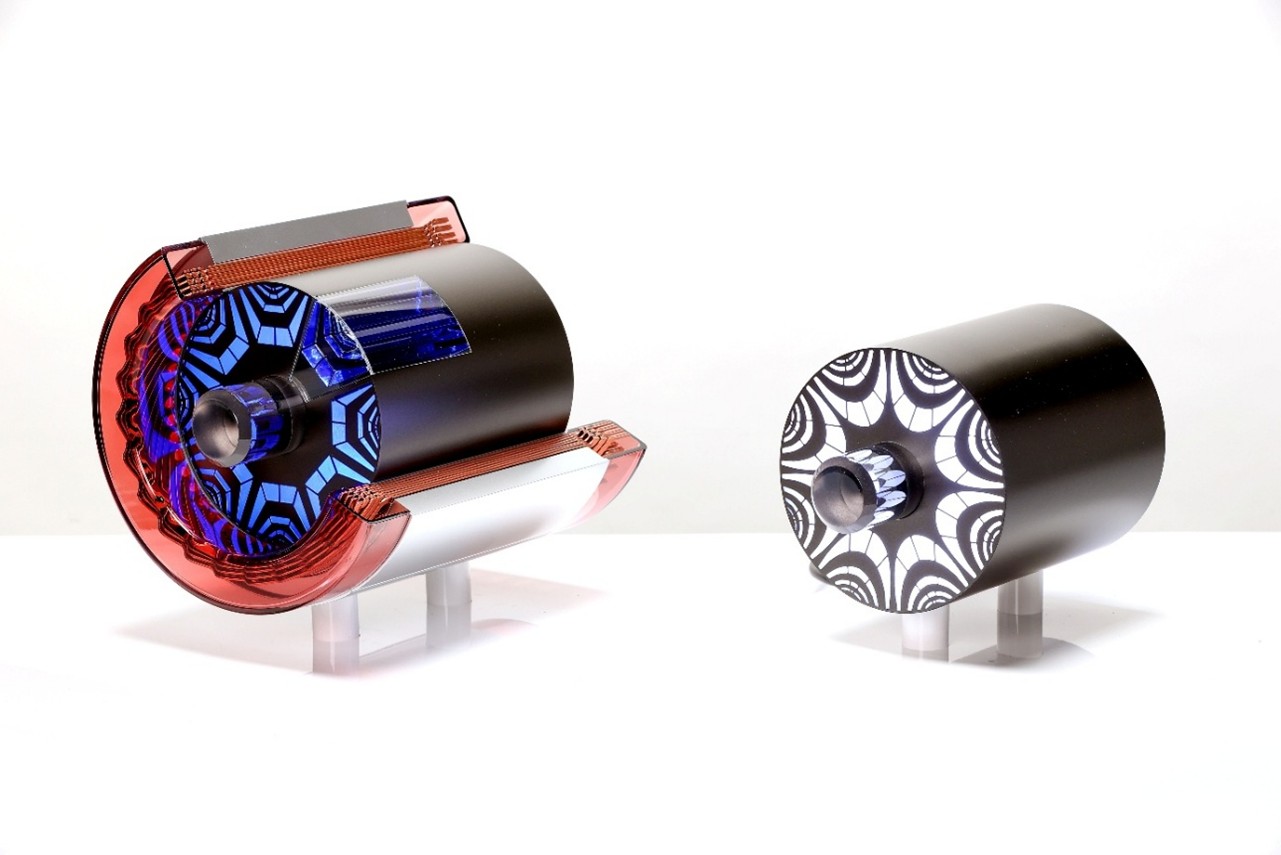 Mockup of the new motor (left: main drive stator & rotor, right: auxiliary drive rotor)
Mockup of the new motor (left: main drive stator & rotor, right: auxiliary drive rotor)
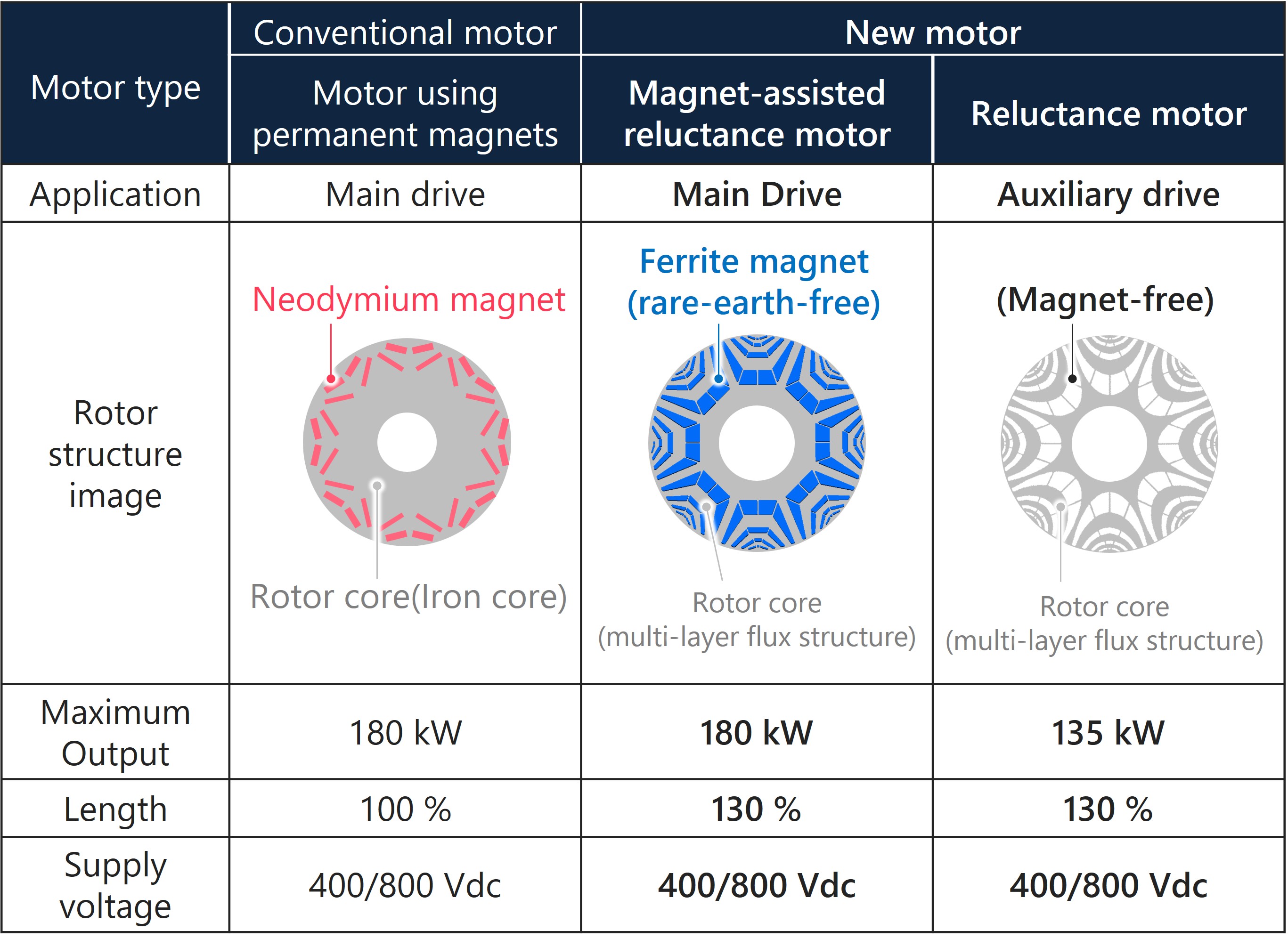
Tokyo, October 27, 2025 – Astemo, Ltd. (hereafter “Astemo”) has developed a new motor for BEVs*1 that significantly reduces resource risks by eliminating the use of rare earth elements.*2 Employing a synchronous reluctance motor system that generates rotational force by inducing magnetism in a rotating rotor (iron) core, it achieves high output by incorporating rare-earth-free magnets into the main drive motor, which is used continuously for propulsion. This enables the replacement of conventional permanent magnet motors in BEV drive systems, which use large amounts of rare earth elements. In this development, the main drive motor—designed to generate driving force continuously—achieved a high output of 180 kW by embedding rare-earth-free magnets. For the auxiliary drive motor used for power assist, a synchronous reluctance motor was combined to eliminate energy loss during coasting rotation, covering a total output of 315 kW. Synchronous reluctance motors are targeted for practical application around 2030, and their adoption in mass-produced vehicles would be a world first*3.
-
*1 BEV
: Battery Electric Vehicle
-
*2 The 17 elements primarily found in periods 4 through 6 of the periodic table.
-
*3 As of October 2025, according to Astemo.
Conventional BEV motors rely heavily on permanent magnets in the rotor—made from rare earth elements like neodymium (neodymium magnets)—to generate strong magnetic fields. However, rare earth entails significant geopolitical risks, and ensuring a stable supply has been a challenge. On the other hand, rare-earth-free ferrite magnets while readily available have a magnetic force that is one-third or less. This means the motor would need to be tripled in size to achieve the same output as conventional motors. In response, induction motors and wound field motors have been adopted, which do not use permanent magnets. However, since these use electromagnets to generate the rotor's magnetic force, they require significant amounts of copper on the rotor. With the expanding adoption of renewable energy and electric vehicles, this presents a possible resource risk for induction and wound field motors with potential copper supply shortages.
Therefore, Astemo developed a new synchronous reluctance motor as a sustainable alternative. This new motor generates rotational force by utilizing differences in magnetic resistance (reluctance) based on the shape of the rotor core. By developing “a multi-layer flux” structure that divides the magnetic force transmission path into multiple layers and precisely controlling the current to form magnetic poles within the rotor core section, it can compensate for the powerful magnetic force generated by neodymium magnets. Forming magnetic poles in the rotor core requires higher current flow through the coils of the stator, which is the fixed part of the motor, posing a challenge with coil heating. Astemo has successfully suppressed increased heat generation within the motor by developing a structure that immerses the slots and ends containing the coils in cooling oil.
Regarding power output, for the main drive motor used continuously in BEVs, a magnet-assisted synchronous reluctance motor incorporating ferrite magnets as an auxiliary element achieves an output of 180 kW while constraining the size increase to 30 percent compared to conventional rare-earth permanent magnet motors. For the auxiliary drive motor, we developed a synchronous reluctance motor that uses no magnets at all. Since embedded magnets in the auxiliary drive can act as a braking force during coasting rotations of the main drive rotor, this would result in an energy loss. Hence, the auxiliary drive operates only when needed for power assistance up to 135 kW, curbing the overall power consumption of the entire BEV drive system.
 Comparison of conventional permanent magnet motors and the new synchronous reluctance motors
Comparison of conventional permanent magnet motors and the new synchronous reluctance motors
The newly developed rare-earth-free motor delivers performance equivalent to conventional BEV motors while strengthening Astemo's electric powertrain portfolio. It reduces procurement risks and price volatility associated with scarcely available resources like rare earths, enabling a stable motor supply. Furthermore, by reducing energy loss across the entire BEV drive system—including both main and auxiliary drives—it curbs power consumption across a wide range of driving scenarios.
The newly developed synchronous reluctance motor will be exhibited at Japan Mobility Show 2025, held at Tokyo Big Sight from October 30, 2025.
Astemo will continue to advance technological development that enhances the value of next-generation mobility, and contribute to the realization of a sustainable society and enriched lives by providing advanced mobility solutions that are highly efficient and reduce our environmental impact.
About Astemo
-
Astemo, headquartered in Tokyo, Japan, is a joint venture between Hitachi, Ltd., Honda Motor Co., and JIC Capital, Ltd. With 80,000 employees worldwide and operations in the Americas, Asia, China, Europe and Japan, the company is a global mega-supplier in the automotive industry. The Electric Business Division, Vehicle Business Division, and Motorcycle Business Division are engaged in the development, manufacture, sales, and service of automotive parts as well as transportation and industrial machinery and systems. Astemo is committed to creating a sustainable society and delivering enhanced corporate value.
For more information, visit: www.astemo.com